When accelerating a vehicle, some noise is normal. However, if there is a sudden loud noise or new unusual sounds, it is crucial to identify the root cause. This is often a sign of aging or worn-out parts. Ignoring the issue can lead to significant damage to the vehicle and may even pose a serious risk to safety. In this article, we will introduce the 9 factors that could cause unusual noises when accelerating a car, ranked by their importance and urgency.
1. Vroom! Engine Noise – Potential Engine Problems
- Importance: High
- Urgency: High
Engine noise is normal, but when the sound becomes unusually loud or produces strange noises, it may be a sign of potential engine problems. For example, low engine oil, worn parts, or other mechanical failures. Over time, the differential gears can wear out, affecting the engine’s performance. This noise usually comes from the top or inside of the engine and is often the result of friction or collision between the various components.

Other Symptoms:
Engine temperature rises
Engine runs unevenly, potentially stalling
Accompanied by metallic grinding or vibration sounds
Solutions:
Check the engine oil level and ensure the oil is in good condition. Regularly replace the engine oil to maintain an adequate level.
If the oil quality has deteriorated or the level is low, top it up or change it promptly.
If internal engine components show signs of wear, a professional technician should carry out repairs or replacements.
Is it safe to drive?
It’s not recommended to drive for extended periods, especially if the engine temperature is too high or the engine runs unevenly. Arrange for repairs as soon as possible to prevent further, more severe engine damage.
2. Knock! Wrong Gasoline Octane – Engine Knock
- Importance: High
- Urgency: High
If you hear a knocking or pinging sound, like marbles bouncing inside the engine, it typically indicates engine knock. This occurs when the fuel in the engine doesn’t burn properly, often due to using gasoline with an octane rating lower than what the vehicle requires. The faster combustion rate causes abnormal pressure to build up in the cylinders, leading to the knocking sound, usually coming from the upper engine, particularly the cylinder area.

Other Symptoms:
Engine vibration or shaking
Reduced power and increased fuel consumption
Check engine light appears
Solutions:
Check your vehicle’s manual to confirm the recommended octane rating for gasoline.
Switch to the correct octane fuel as specified by the manufacturer.
If knocking persists, have a professional technician check the ignition timing and knock sensors.
Is it safe to drive?
While the issue may not cause immediate harm, prolonged engine knock can severely damage the engine. It’s important to switch to the appropriate fuel and have the vehicle inspected promptly.
3. Clunk! Transmission Noise – Gearbox or Clutch Issues
- Importance: High
- Urgency: Medium
If you hear a loud or unusual “clunk” noise when accelerating or shifting gears, it could indicate that your clutch is worn out or there’s a deeper issue with the transmission. This noise typically comes from the gearbox area located underneath the vehicle. The cause of the noise may be worn gears, dirty or low transmission fluid.
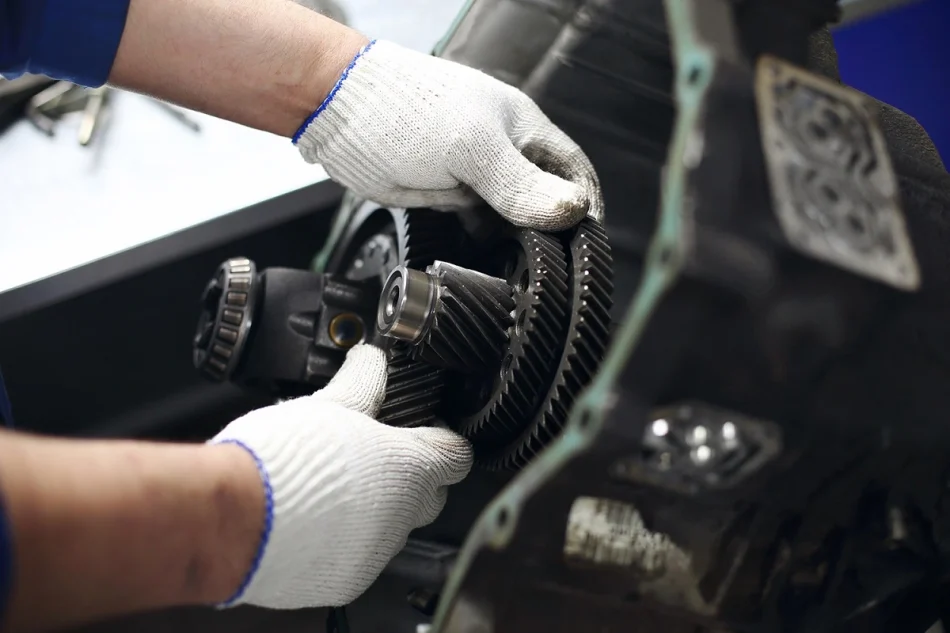

Other Symptoms:
Difficulty or stiffness when shifting gears
Elevated transmission temperature
Vehicle shaking or unable to drive smoothly during engine acceleration
Solutions:
Check the transmission fluid level and quality to ensure it’s adequate and clean.
Regularly replace the transmission fluid, especially when reaching the manufacturer’s recommended mileage.
Inspect the gears and clutch for wear; if worn or faulty, have them repaired or replaced immediately.
Is it safe to drive?
If you experience severe shifting issues or unusual noises, it’s best not to continue driving. Visit a repair shop immediately to have your transmission checked to avoid compromising driving safety.
4. Whine! Differential Noise – Possible Gear Wear
- Importance: High
- Urgency: Medium
If you hear a whining noise when accelerating or turning, it may be due to worn gears or insufficient lubricant in the differential. This sound typically originates from the rear of the vehicle or near the driveshaft.
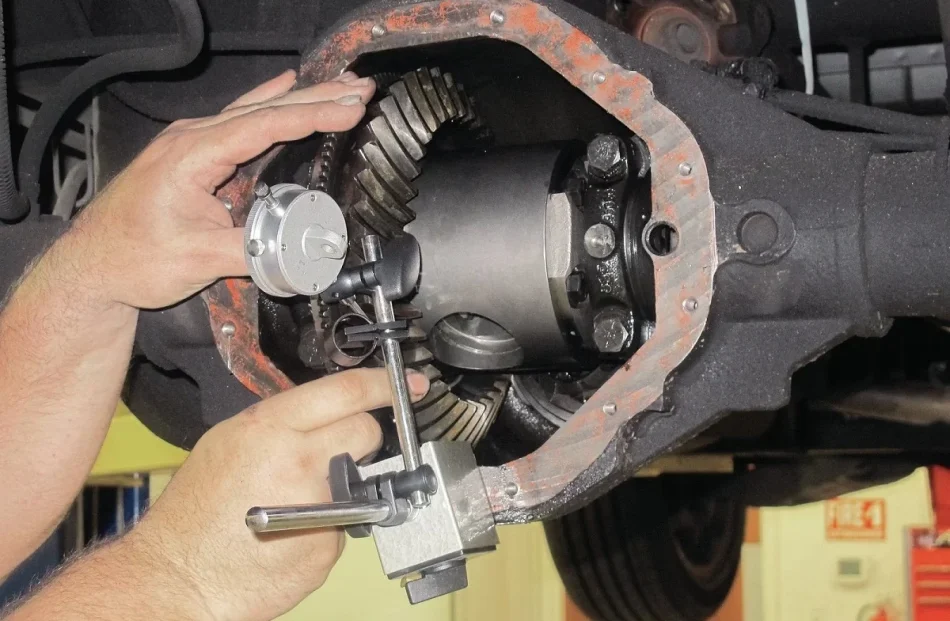
Other Symptoms:
Continuous whining or grinding noise
Noise becomes more noticeable during turns
Uneven power transmission, possibly causing the vehicle to behave erratically
Solutions:
Check the differential fluid level and quality to ensure it’s adequate and not contaminated.
If the fluid is low or poor quality, replace it with fresh fluid.
Inspect the differential gears for wear, and replace any severely worn gears as necessary.
Tips:
The frequency of differential fluid changes depends on the vehicle type:
For regular passenger cars, changing the fluid every 30,000 to 50,000 kilometers is ideal.
For vehicles used for frequent off-roading, towing, or high-performance driving, it’s recommended to change the fluid every 20,000 to 30,000 kilometers.
For modified vehicles with LSD (Limited Slip Differential), it’s best to follow the manufacturer’s recommendation for regular differential fluid changes.
However, early fluid replacement is necessary if:
The vehicle is regularly submerged in water, or water may have entered the differential.
Internal components, like LSD or gear sets, have been replaced.
Is it safe to drive?
If the differential noise persists or worsens, it’s recommended to repair or replace the differential promptly to avoid more extensive damage or power transmission issues.
5. Squeaking or Squealing – Worn Serpentine Belt
- Importance: High
- Urgency: Medium
The serpentine belt in your engine helps power various components of the vehicle. However, over time, the belt may wear out or become damaged. If you hear a sharp squeaking or squealing noise while accelerating, it could be due to a worn or slipping belt. This typically occurs after the vehicle has been in use for about five years. Belt-related noises generally come from the front of the engine.
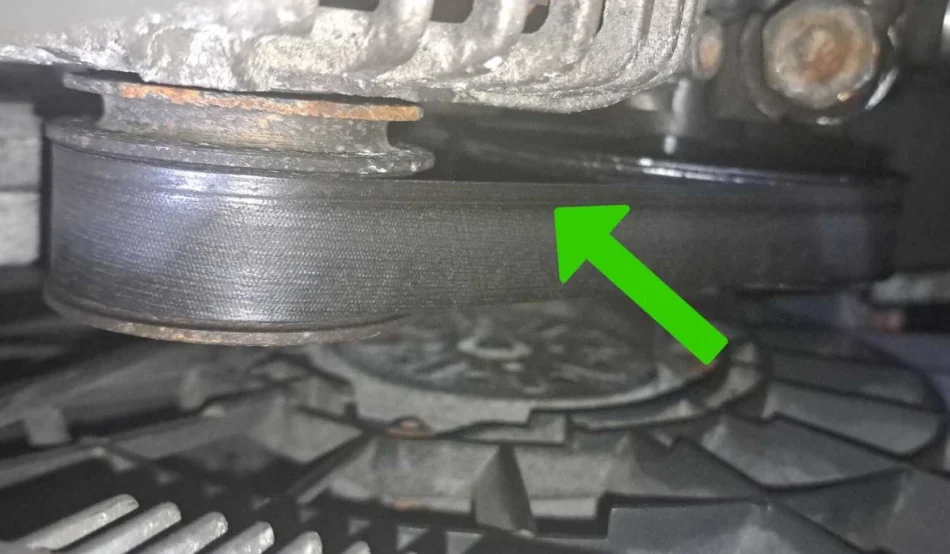

Other Symptoms:
Cracks or wear on the belt
Decreased engine performance or overheating
Unusual noises when starting the engine
Solutions:
Inspect the belt for cracks or wear. If the belt is damaged, replace it as soon as possible.
Regular belt inspections should be done, especially if the vehicle is older than five years.
If the belt looks fine, check the pulleys for wear or loosening. If necessary, have a technician inspect the system.
Is it safe to drive?
If you hear belt noise while driving, it’s best to address it as soon as possible. Worn belts can lead to damage to other components, causing further breakdowns.
6. Rattle! Exhaust Noise – Leaks or Muffler Damage
- Importance: Medium
- Urgency: Medium
If you hear a metallic rattling or vibrating sound while accelerating, it’s often due to a loose exhaust pipe, a leak, or damage to the muffler. Over time, the exhaust system can deteriorate, rust, or become loose due to accidental impacts. The noise is typically located underneath the vehicle, especially near the rear exhaust area.
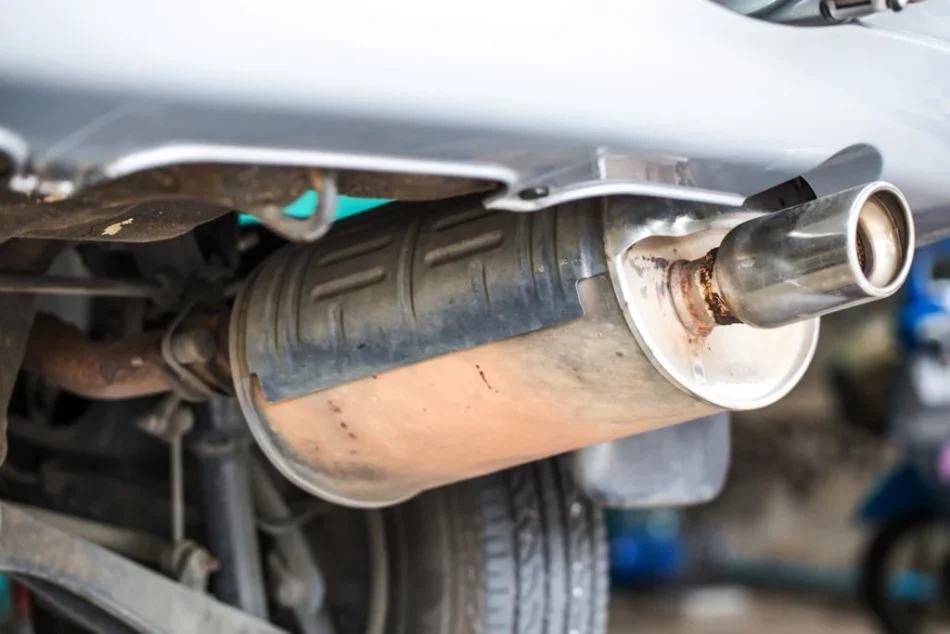

Other Symptoms:
Louder, deeper exhaust sounds
Unusual exhaust smell or noticeable odd noises, potentially including a rotten egg odor
Increased fuel consumption, decreased power
Solutions:
Inspect the exhaust pipe for cracks, detachment, or rust.
Replace damaged exhaust pipes or repair the muffler.
Check the exhaust hangers and brackets to ensure they are securely fastened.
Is it safe to drive?
Minor leaks may allow for short-term driving, but serious leaks or detachment require immediate repair to prevent harmful gas leaks or engine performance issues.
7. Hiss! Vacuum or Hose Issue – Leaks in Vacuum System
- Importance: Medium
- Urgency: Medium
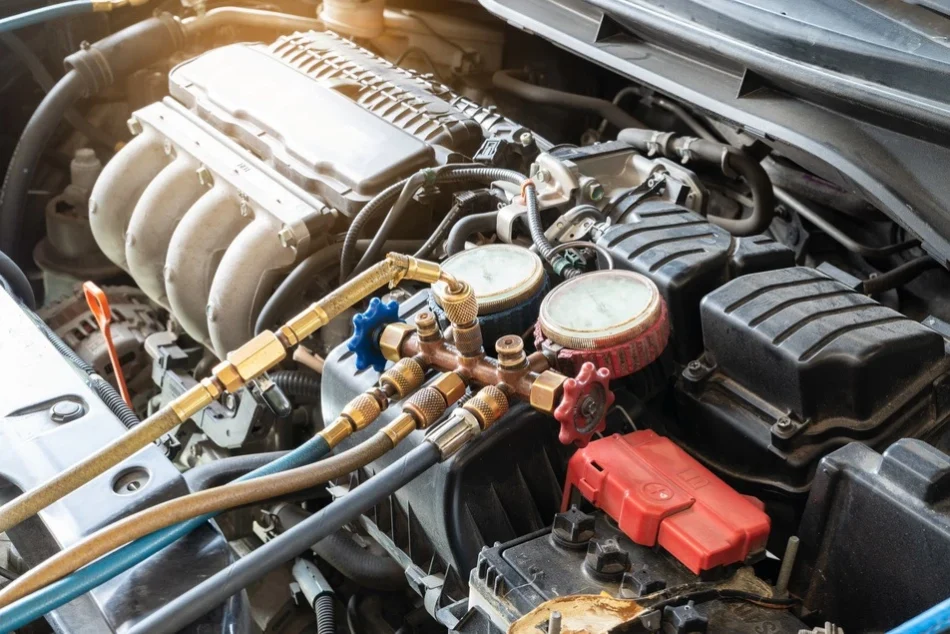

If you hear a hissing sound while accelerating, it’s likely caused by a vacuum system or hose leak. Over time, vacuum hoses can deteriorate, crack, or loosen, allowing air to enter areas it shouldn’t, which can affect engine performance. This issue is more common in older vehicles, so it requires more frequent attention. The hissing sound generally comes from within the engine bay.
Other Symptoms:
Unstable idle, with fluctuating RPMs
Slow or delayed throttle response
Check engine light illuminates
Solutions:
Inspect vacuum lines and hoses for cracks, looseness, or aging.
Replace damaged hoses or re-secure any loose connections.
Use a smoke machine to detect small leaks in the system.
Is it safe to drive?
Minor leaks may allow for short-term driving, but to ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency, it’s recommended to repair the issue as soon as possible.
8. Growl! Loose Wheel Bearings – Worn or Damaged Bearings
- Importance: Medium
- Urgency: Medium
If you hear a low growling sound while accelerating or turning, it may be caused by worn or loose wheel bearings. As the bearings wear down, abnormal friction occurs between the tire and wheel support, leading to the noise. The sound generally originates from the wheel area, and the noise increases as you accelerate, causing the bearings to spin faster.
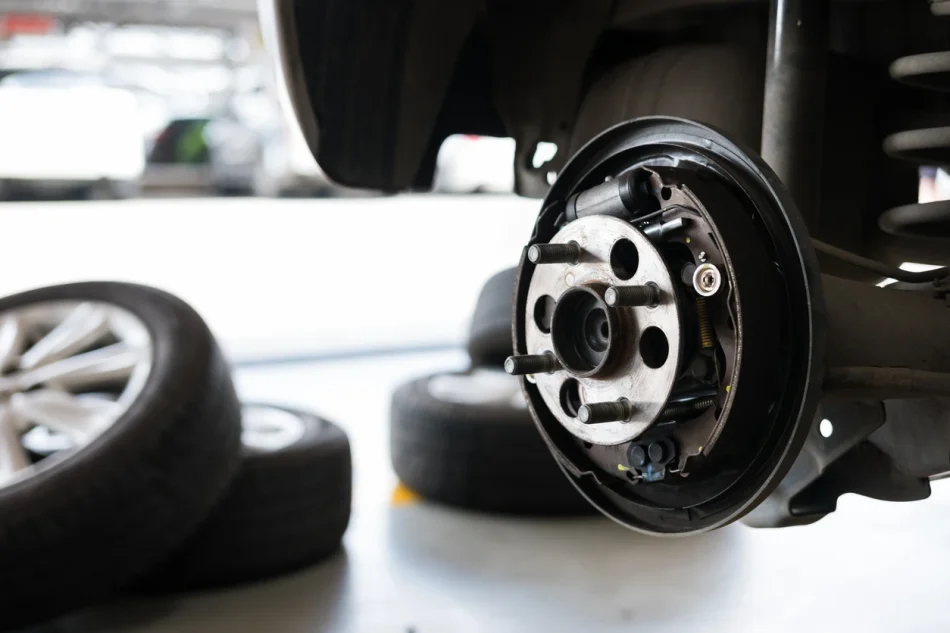

Other Symptoms:
Increased noise from the wheel area, especially when turning
Steering wheel vibrations or diminished handling
Uneven tire wear
ABS warning light illuminated
Solutions:
Inspect the condition of each wheel bearing.
If the bearings are loose or have excessive play, replace them with new bearings immediately.
Regularly check and maintain the suspension system to ensure proper performance.
Is it safe to drive?
It’s not advisable to continue driving, especially if the bearing noise is noticeable. Continuing to drive may result in tire detachment, which presents a serious safety risk.
9. Thump! Tire Noise – Uneven Tread or Road Surface Issues
- Importance: Medium
- Urgency: Low
If you hear a rhythmic thumping sound from underneath the vehicle while accelerating or driving at high speeds, and the noise becomes louder during acceleration or turns, the issue may be with one of your tires. This typically indicates problems like tread separation, sidewall bulges, or even a flat spot on the tire.
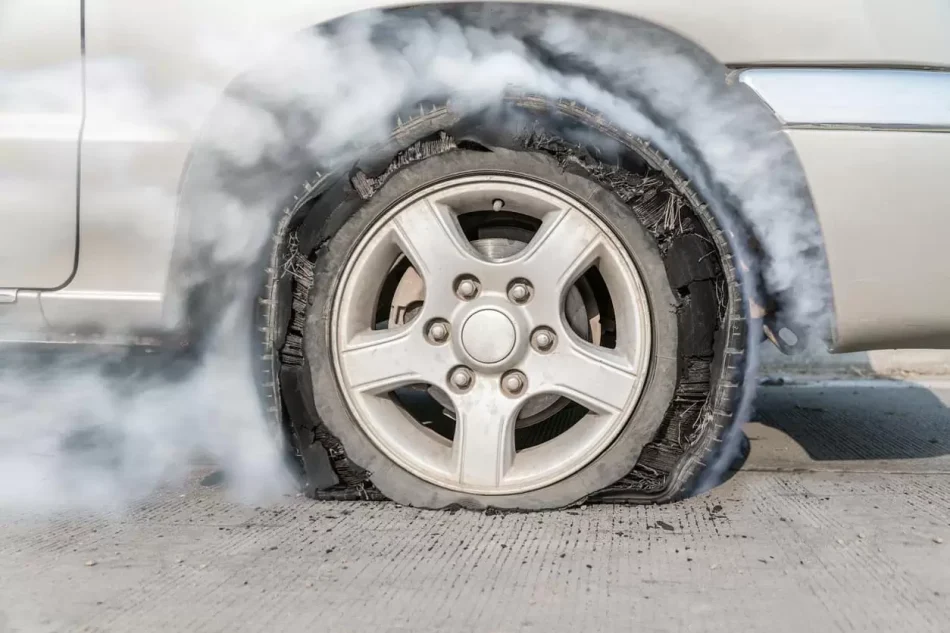

Other Symptoms:
Steering wheel vibrations while driving
Vehicle pulling to one side
Visible signs of tire wear
Solutions:
Inspect the tires for uneven wear; replace them if they show signs of significant wear or damage.
Regularly perform wheel alignment and balancing to ensure proper tire wear.
Maintain correct tire pressure and rotate the tires regularly to extend their lifespan.
Is it safe to drive?
In most cases, driving is possible, but if the tire shows severe wear or poses a risk of blowout, it should be replaced immediately to ensure driving safety.

